|
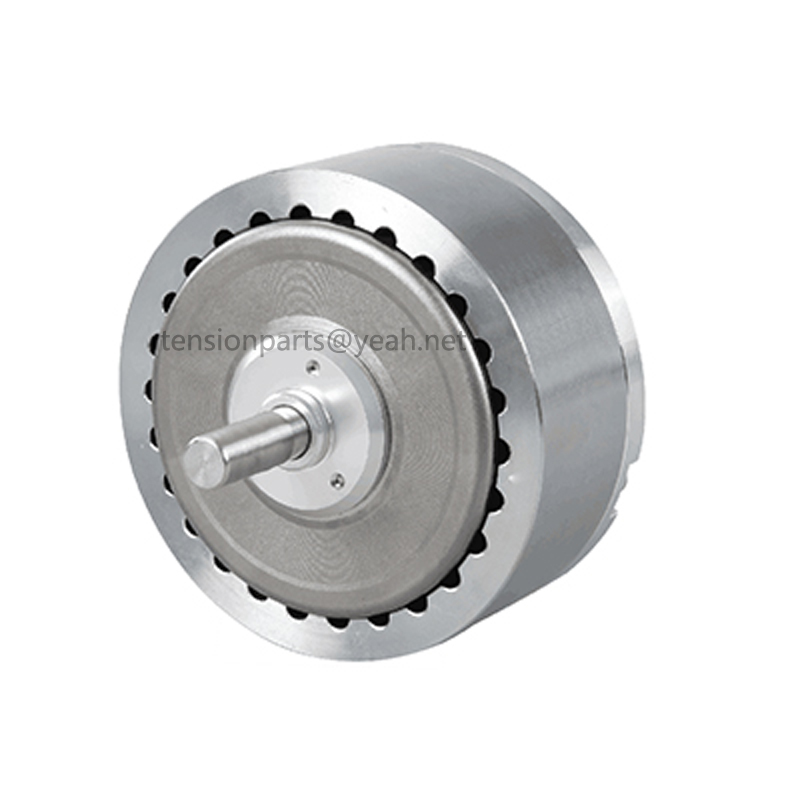
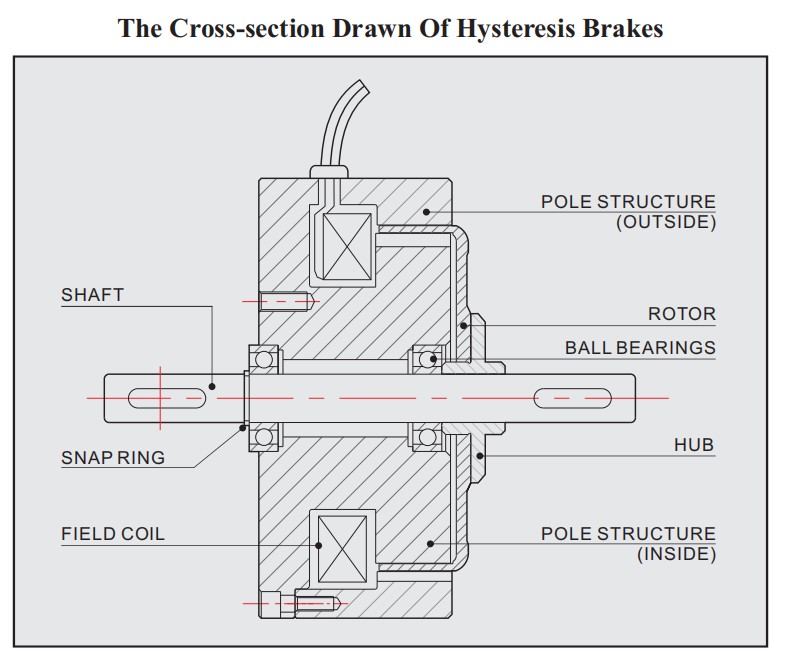
Hysteresis Brakes Selection GuideOverview Hysteresis Brakes produce torque strictly through a magnetic air gap without the use of magnetic particles or friction components.This method of braking provides far superior operating characteristics (smoother torque, longer life, superior repeatability, high degree of controllability, and less maintenance and down time) which make them the preferred choice for precise tension control during the processing of nearing any meterial, web or strand. Structural Characteristics The hysteresis effect in magnetism is applied to torque control by the use of two basic components - a reticulated pole structure and a specialty steel rotor/shaft assembly - fastened together but not in physical contact. Until the field coil is energized,the drag cup and shaft can spin *ly on its bearings. When a magnetizing force from either a field coil or magnet is applied to the pole,structure,the air gap becomes a flux field. The rotor is magnetically restrained,providing a braking action between the pole structure and rotor. Operating Principles The Hysteresis Brake provides torque by the use of two basic components—a reticulated pole structure and a specialty steel rotor/shaft assembly—fitted together but not in physical contact. Until the pole structure is energized, the drag cup can spin *ly on its shaft bearings. When a magnetizing force from the field coil is applied to the pole structure, the air gap becomes a flux field and the rotor is magnetically restrained, providing a braking action between the pole structure and rotor.
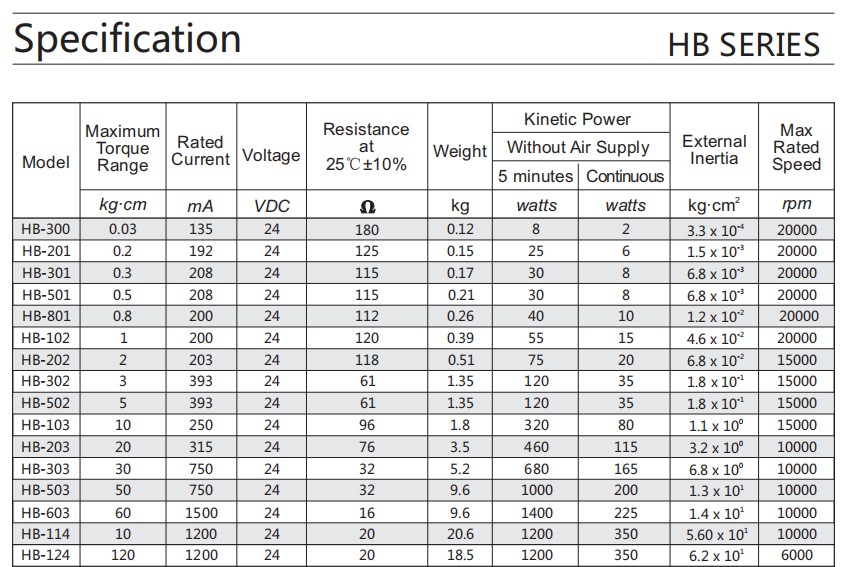
Model Selection
|









 ICP:2022111349-1
ICP:2022111349-1